History
Service and demise
SMS Mainz was launched as one of four Kolberg-class light cruisers on 23rd January 1909 at the AG Vulcan shipyard in Stettin. At the outbreak of World War I the vessel was assigned to patrols off the island of Heligoland in the II Scouting group (II. Aufklärungsgruppe).
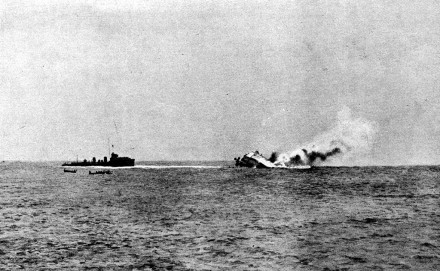
At the Second Battle of Heligoland Bight on 28 August 1914, the German patrol forces were attacked by superior British forces, receiving several damaging hits with gunfire and a torpedo that disabled the Mainz and prompted her commander to abandon ship. 89 crew members died in the battle, while 348 men were rescued by the British before the ship rolled over and sank.

Description
Class: Kollberg-class cruiser.
Yard: AG Vulkan, Stettin.
Propulsion: 2 steam turbines.

SMS Mainz.
| Master | Wilhelm Paschen |
|---|---|
| People on board | 437 |
| Speed | 27 knots ~ 31 mph (50 km/h) |
| Length | 426 ½ feet (130 m) |
| Draft | 18 ¼ feet (5.6 m) |
| Beam | 46 feet (14 m) |
| Displacement | 4889 ton |
Status
The wreck is situated in the German Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ). Due to the sovereignty of federal states in cultural politics ('Kulturhoheit der Länder'), the power of the state agencies responsible for heritage protection extends only into territorial waters (the 12 nautical mile zone), and thus heritage protection is not regulated in the German EEZ. However, naval shipwrecks are granted sovereign immunity under international law and remain the property of their state of origin, and as such the German Federal Republic is the inheritor of war wrecks of the Imperial German Navy.
In the years 2011, 2015 and 2016 artefacts were salvaged from the wreck site by members of a Dutch sports diving club. This incident prompted a criminal investigation for the violation of a war grave. Eventually, the divers agreed to return the artefacts, which are now exhibited in the Bundeswehr Museum of Military History in Dresden.
References
- Wikipedia.
SMS Mainz. - Bundeswehr Military History Museum.
- "Das Seegefecht bei Helgoland" (Historical-Archaeological Research Project).
www.seegefecht-helgoland.de. - SPIEGEL (Newspaper).
Bundespolizei ermittelt gegen Wrackplünderer (Federal police investigates wreck looters). - Welt (Newspaper).
Wrack der „SMS Mainz“ vor Helgoland geplündert (Wreck of "SMS Mainz" near Heligoland looted). - Alexander Hammerton. T (1914).
he Great War: The Standard History of the All-Europe Conflict. - C.O. Nordensvan, ed. (1915).
Det stora världskriget.
Det stora världskriget vol. II.
pp 339.